Table of Contents
Preface:
Oil spills constitute a significant environmental catastrophe that can inflict enduring harm on marine ecosystems. Remediation efforts are crucial to mitigate impact; yet, conventional techniques such as chemical dispersants, booms, and skimmers frequently lack efficiency and sustainability. Recently, the emphasis has transitioned to creating environmentally sustainable, economical materials capable of remediating oil spills without causing more ecological damage. Dicholesteryl organogelator is a promising green sorbent nanomaterial capable of successfully absorbing oil and facilitating cleanup. This article examines the synthesis, characteristics, and potential applications of dicholesteryl organogelators for oil spill remediation.
Comprehending Oil Spills:
Oil spills discharge substantial volumes of petroleum-derived materials into the marine ecosystem. The repercussions encompass harm to animals, water contamination, and disturbances to local economies. Remediating large accidents is a multifaceted endeavor, and existing techniques, such as mechanical recovery and chemical dispersants, possess inherent limits. Traditional sorbents, such as synthetic fibers, frequently exhibit inefficiency and may produce secondary waste, exacerbating environmental problems.
What are organogelators?
Organogelators are substances that can create gels in organic solvents. They function by encapsulating liquids within a semi-solid matrix, inhibiting oil dispersion while facilitating easy retrieval. Because of their strong attraction to organic substances like petroleum, they are ideal for oil spill recovery. These materials provide a safer and more efficient substitute for conventional cleaning agents.
Cholesteryl-Derived Organogelators:
We synthesize cholesterol-based organogelators from cholesterol, a naturally occurring lipid. Due to their unique molecular architecture, cholesterol derivatives are known for their ability to form stable gels and their robust interactions with hydrophobic materials like oil. Dicholesteryl organogelators have garnered interest because of their exceptional oil-absorbing capabilities, which provide an eco-friendly remedy for oil spills.
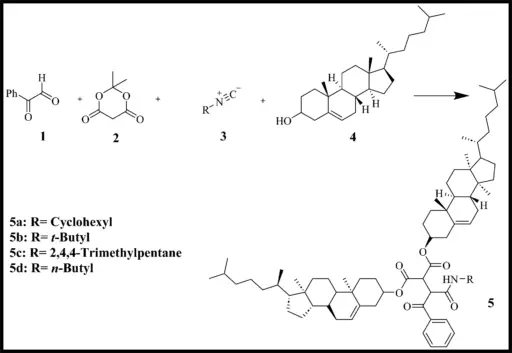
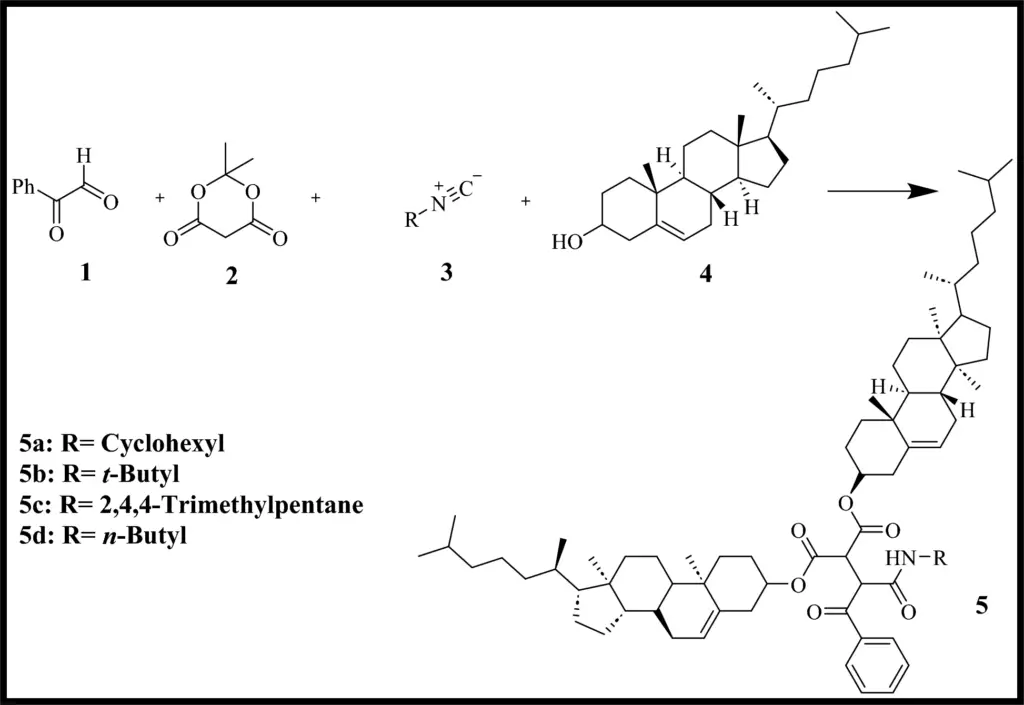
Synthesis of Dicholesteryl Organogelator:
The synthesis of dicholesteryl organogelator is based on green chemistry principles, guaranteeing a sustainable and non-toxic method. As part of the process, cholesterol is often esterified with certain fatty acids or other organic parts. This creates a gelator that can form a stable network that is good at absorbing oil. Essential reactions in this process aim to reduce detrimental consequences, rendering it an environmentally responsible option.
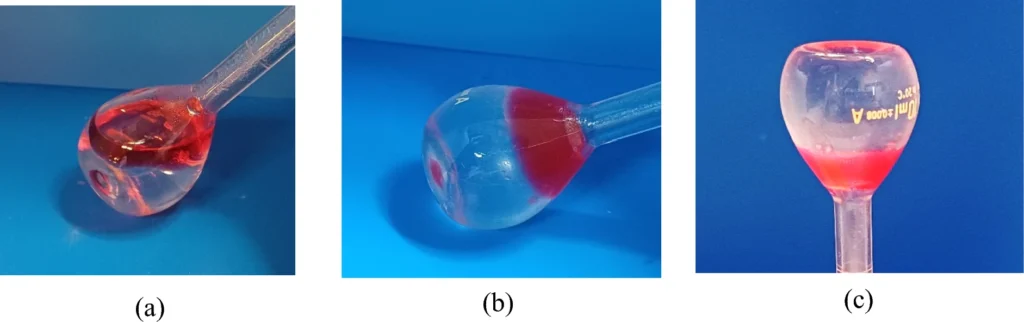
The phase-selective gelation behavior of dicholesteryl gelator 5a in petroleum in the presence of seawater. The gelator is in its (a) solution state, (b,c) gel state
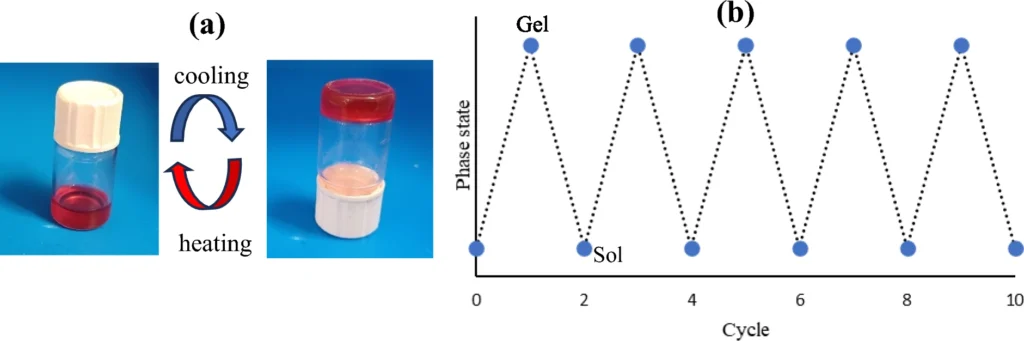
The thermo-reversibility behavior of gel 5a in petroleum (a) solidification by cooling below Tgel and liquefication by heating the gel above its Tgel, (b) The gel-to-solution transition cycle.
Characteristics of Dicholesteryl Organogelator:
Dicholesteryl organogelators exhibit stability and hydrophobicity, rendering them suitable for oil spill remediation. Their molecular configuration enables them to absorb substantial amounts of oil while maintaining structural integrity. Moreover, these organogelators are biodegradable, indicating they will decompose naturally post-use, hence diminishing environmental effects.
Properties of Dicholesteryl Organogelator Nanomaterials:
Dicholesteryl organogelators exhibit remarkable nanoscale properties. Their extensive surface area enhances their oil-absorbing capability, enabling them to absorb more oil than traditional materials. These nanoparticles engage with oil molecules, efficiently encapsulating them within a matrix of hydrophobic fibers.
Mechanism of Oil Absorption:
Dicholesteryl organogelators sequester oil via molecular entrapment. The organogelator establishes a three-dimensional network that entraps oil molecules, resulting in a gel that stabilizes the absorbed oil. This procedure inhibits the oil from disseminating further and facilitates its extraction from the water’s surface.
Dicholesteryl organogelators provide benefits for oil spill remediation:
Dicholesteryl organogelators have a primary benefit in terms of environmental sustainability. In contrast to synthetic sorbents, they are biodegradable and non-toxic, hence preventing pollution during and after the remediation process. Reusing them numerous times makes them a cost-effective remedy for extensive oil spills.
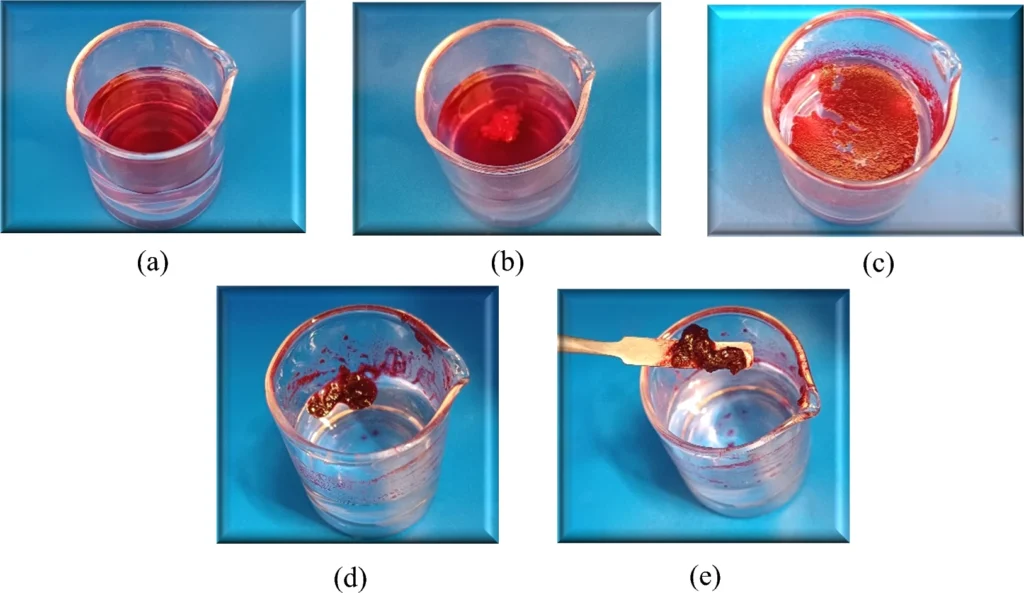
Selective gelation of petroleum in the presence of seawater (a) biphasic solution of 20 ml water and 2 ml petroleum, (b) adding gelator 5a on the water surface, (c) waiting for gelation after dissolving at room temperature, (d) collecting the gelled oil by spatula in one side, (e) removing the gel from the water surface (cleaning the surface of the seawater from petroleum).
Case analysis and research outcomes:
Recent research has demonstrated the efficacy of dicholesteryl organogelators in oil spill scenarios. Laboratory investigations have demonstrated that these materials can absorb up to 20 times their own weight in oil, rendering them significantly more efficient than conventional sorbents. In practical applications, they have demonstrated significant efficacy in reducing the environmental consequences of oil spills.
Decomposability and ecological consequences:
The biodegradable properties of dicholesteryl organogelators represent a substantial environmental advantage. Upon absorption of the oil, these components decompose naturally over time, resulting in no deleterious leftovers. This renders them an optimal selection for environmentally aware oil spill repair initiatives, as they assist in mitigating prolonged ecological harm.
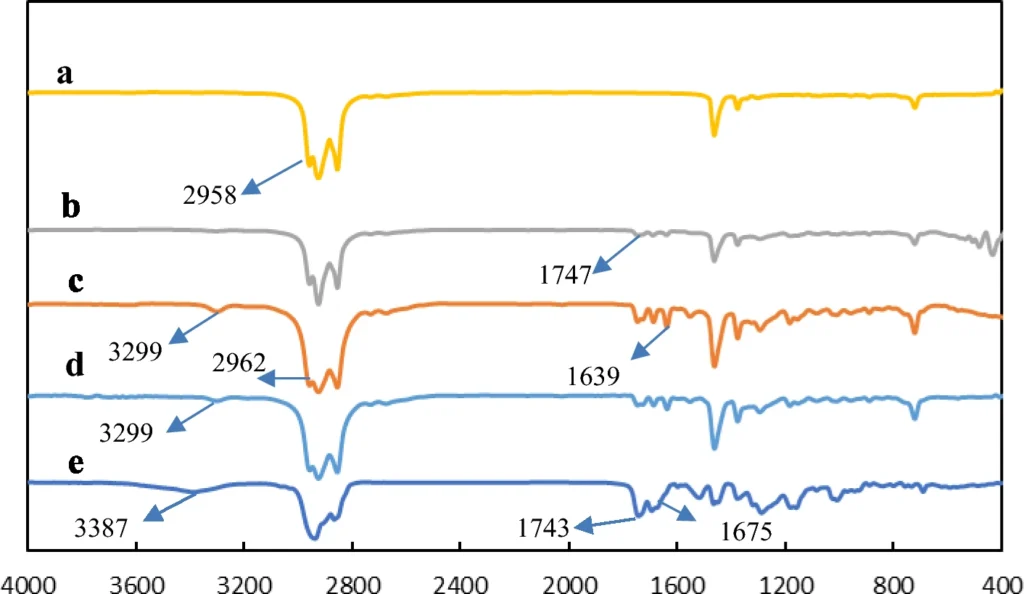
FT-IR spectra of (a) solvent, (b) solution, (c) gel 10% (w/v), (d) gel 25% (w/v), (e) powder of dicholesteryl gelator 5a
Obstacles and prospective pathways:
Regardless of their potential, problems must be addressed before dicholesteryl-organogelators can be widely used for large-scale oil spill remediation. A primary problem is increasing output to meet the requirements of large oil disasters. Future research seeks to optimize the synthesis process and augment the performance of these materials to increase their efficacy.
Prospect for Extensive Implementation:
The prospects for widespread use of dicholesteryl organogelators are encouraging. These materials are comparatively cost-effective to manufacture, particularly in relation to other advanced oil remediation techniques. Their reusability further decreases expenses, rendering them a feasible solution for managing extensive oil spills in marine ecosystems.
Comparison of Dicholesteryl Organogelator with Alternative Green Sorbents:
Dicholesteryl organogelators offer distinct advantages over other green sorbents, such as biochar and cellulose-based materials, in oil spill recovery. Their exceptional oil-absorbing capability, along with biodegradability and reusability, distinguishes them as an optimal selection for environmentally sustainable oil spill remediation.
Final Assessment:
Dicholesteryl organogelators constitute an innovative, environmentally friendly approach to the persistent issue of oil spill remediation. Their distinctive attributes, including elevated oil absorption capacity, biodegradability, and user-friendliness, render them an optimal substitute for conventional oil remediation techniques. Continued research and development in this field could produce materials that are more efficient and cost-effective, ensuring the environmentally sustainable handling of future oil spills.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1). What is the importance of dicholesteryl organogelators in oil spill remediation?
Dicholesteryl organogelators are a biodegradable and environmentally friendly alternative to cleaning up oil spills that can absorb a lot of oil with fewer negative effects on the environment.
2). What mechanism do organogelators use to absorb oil?
Organogelators create a three-dimensional network that encloses oil molecules within its structure. This stops the oil molecules from spreading further and makes it easy to retrieve.
3). Are dicholesteryl-organogelators ecologically sustainable?
Indeed, they are biodegradable and non-toxic, rendering them an environmentally friendly option for oil spill repair.
4). Are dicholesteryl organogelators reusable upon oil absorption?
In fact, their reusability makes them a cost-effective solution for large-scale oil spills.
5). What advantages do cholesteryl-based organogelators possess over conventional oil spill remediation techniques?
They possess superior oil absorption ability, are biodegradable, and do not contribute to secondary pollution, in contrast to synthetic materials.
For more chemistry blogs, visit chemistry Master