Table of Contents
An overview of Gaucher disease:
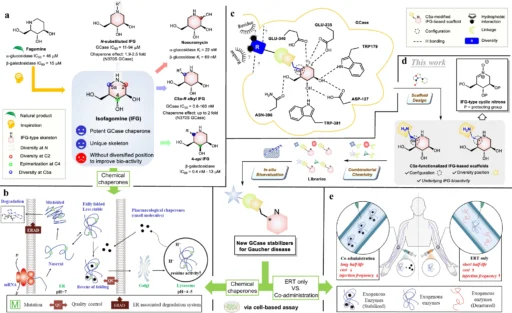
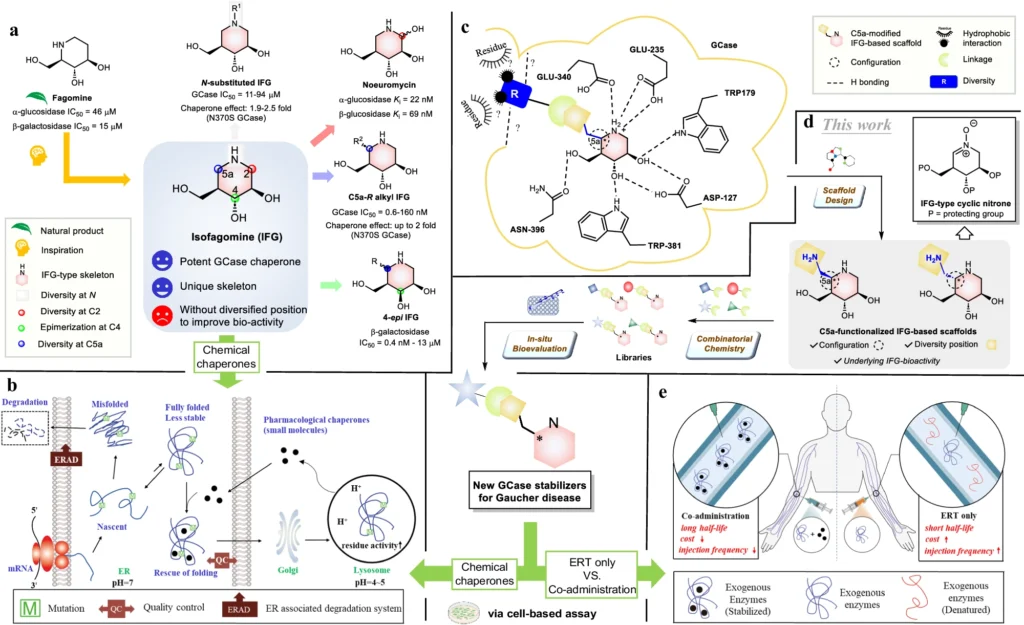
The treatment of Gaucher illness, a rare genetic ailment, is particularly challenging due to the absence of efficacious medicines. The condition is a result of an insufficiency of the enzyme glucocerebrosidase, which causes the buildup of glucocerebroside in cells and tissues. This accumulation leads to a variety of symptoms, including enlargement of the liver and spleen, abnormalities in the bones, and a decrease in the number of red blood cells. Enzyme replacement therapy and substrate reduction therapy are the current treatments for Gaucher disease. However, these methods have difficulties in fully treating all components of the disease pathology. Design and general strategy to discover new GCase stabilizers for potential treatment of Gaucher disease.
The Significance of Protein Stabilizers:
Protein stabilizers are essential in the management of Gaucher’s illness since they aid in the correct folding and functioning of defective glucocerebrosidase enzymes. These stabilizers have the potential to enhance enzyme stability, boost catalytic activity, and improve lysosomal trafficking, resulting in improved treatment results for patients. Nevertheless, the task of creating protein stabilizers that are efficient for treating Gaucher’s illness is still difficult, which means that it is necessary to investigate new techniques and molecular frameworks.
Nitrone-derived isofagomines functionalized with C5a:
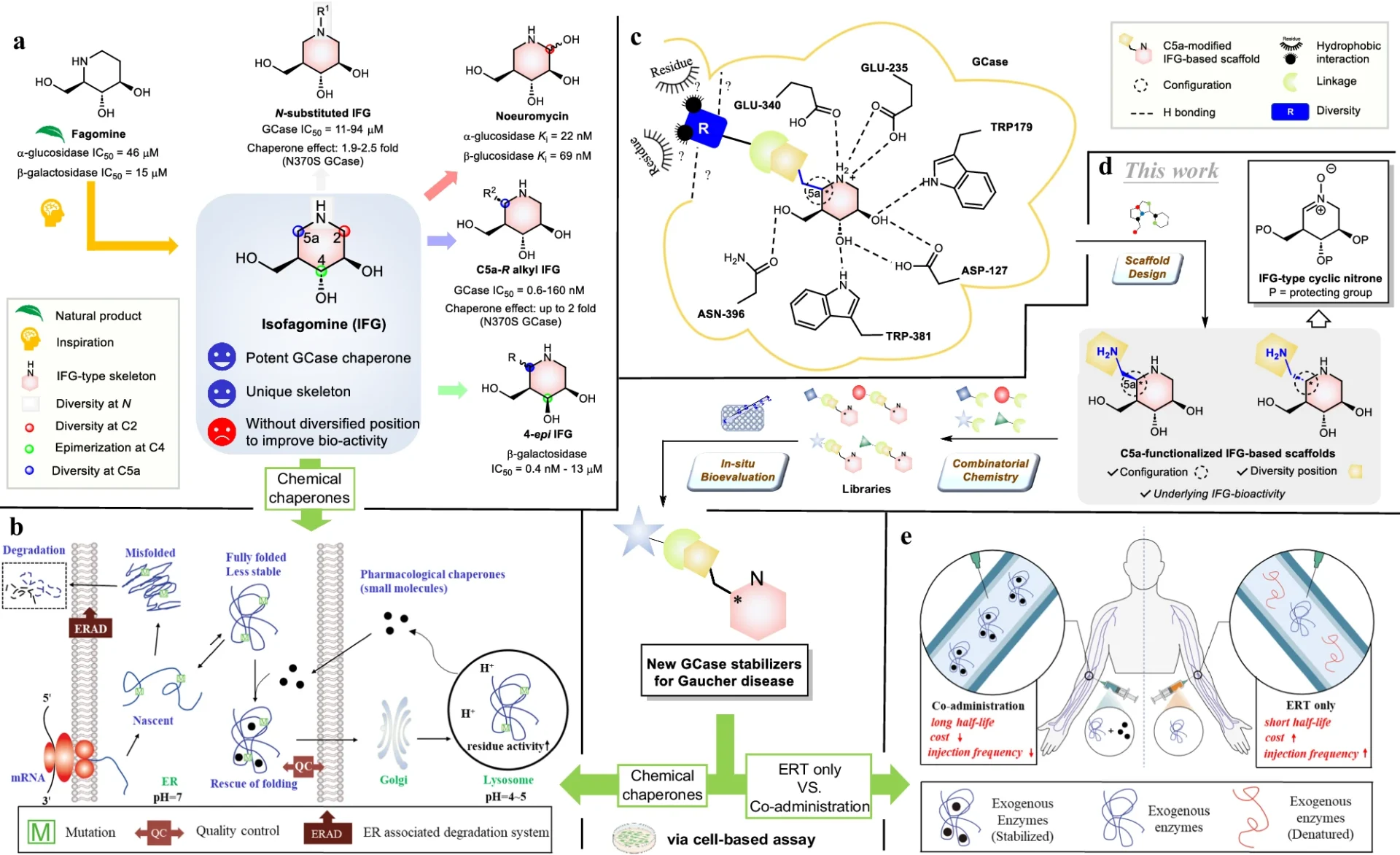
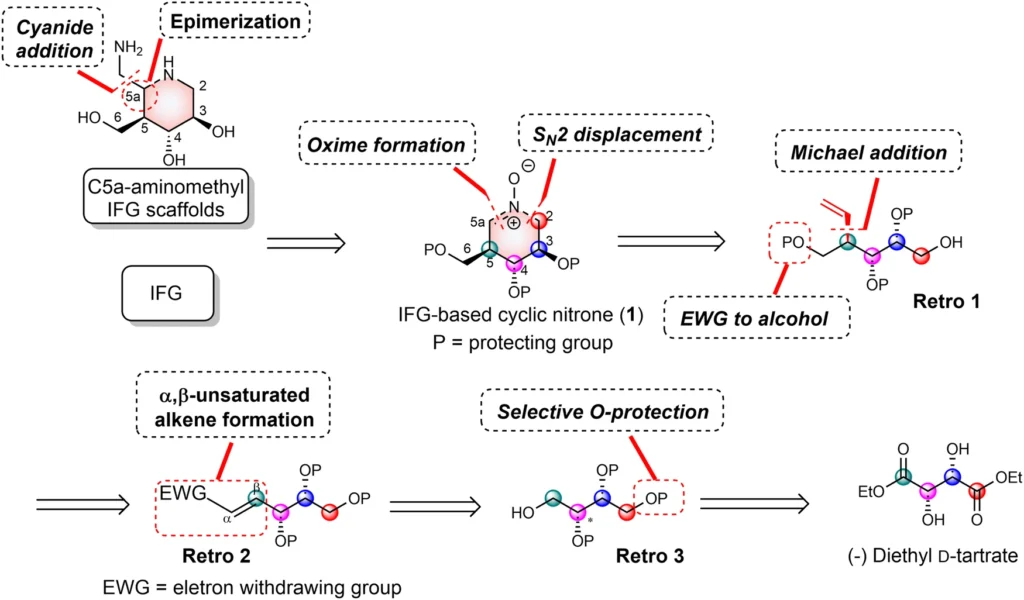
An encouraging approach to treatment involves utilizing nitrone-derived C5a-functionalized isofagomines as agents to stabilize proteins. These chemicals exhibit promise as pharmacological chaperones, with the ability to stabilize misfolded proteins and facilitate their correct folding and functioning. Nitrone-derived isofagomines provide a focused method for stabilizing proteins in Gaucher disease therapy by selectively targeting particular parts of the enzyme structure, such as the active site and stability domains. Retrosynthetic analysis of C5a-aminomethyl IFG-based scaffolds and cyclic nitrone:
Synthesis of compound libraries and evaluation of selected compounds:
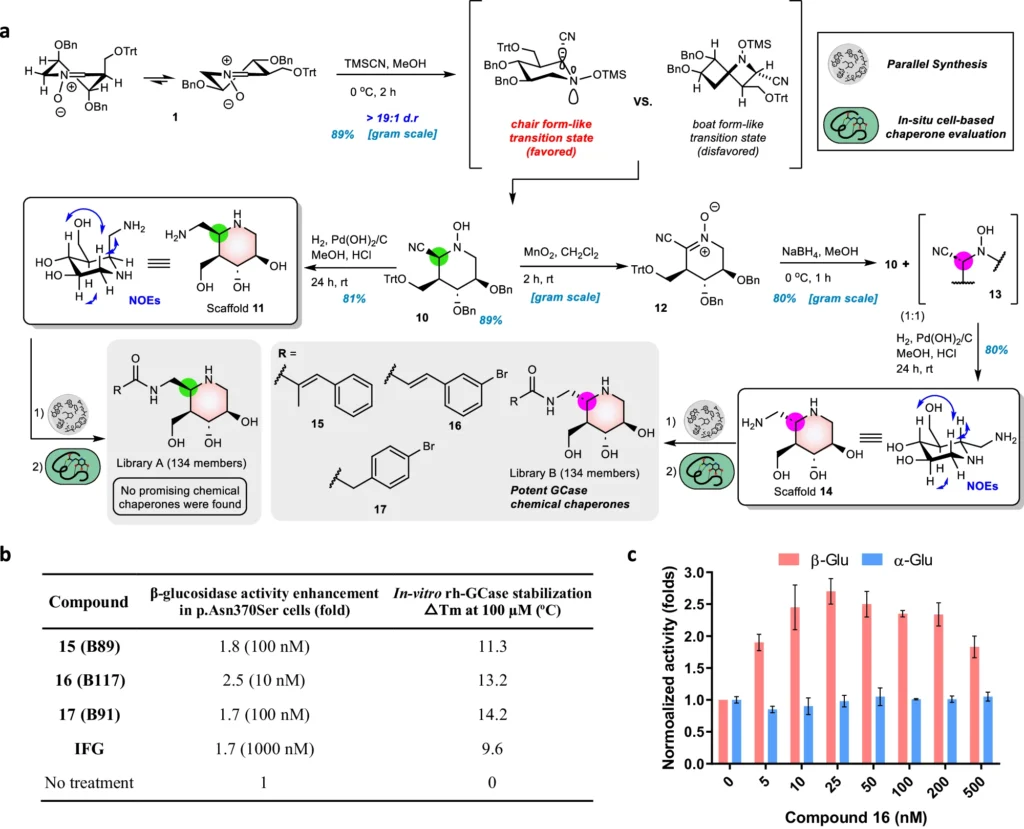
Efficient Synthesis Approach:
The process of creating nitrone-derived C5a-functionalized isofagomines comprises a meticulously planned sequence of procedures to construct the molecular framework and incorporate functional groups at precise locations. Important reactions involve the creation of the isofagomine core, followed by the addition of the nitrone and C5a-functionalized components. Accurate manipulation of reaction conditions and careful selection of reagents are necessary at every stage of the synthesis process to guarantee optimal production yields and the purity of the end product.
Utilizations in the Treatment of Gaucher Disease:
After being created, nitrone-derived C5a-functionalized isofagomines can be assessed for their effectiveness as protein stabilizers in both preclinical and clinical trials. These chemicals can enhance the stability and efficacy of mutant glucocerebrosidase enzymes, resulting in improved therapy results for individuals with Gaucher disease. In addition, their specialized mechanism of action may decrease unintended effects and improve the precision of stabilizing enzymes. Structures of resynthesized IFG derivatives and bioevaluation results:
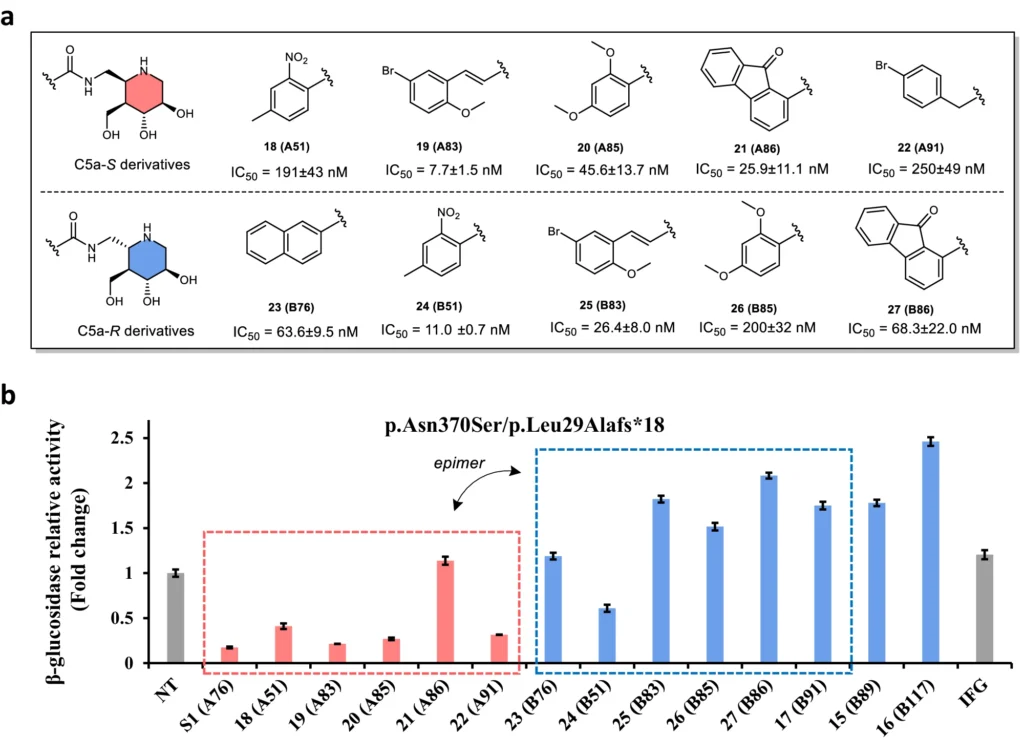
In conclusion:
Overall, the efficient production of nitrone-derived C5a-functionalized isofagomines shows potential for creating protein stabilizers for the management of Gaucher disease. These chemicals have the potential to enhance the stability and performance of mutant glucocerebrosidase enzymes by specifically targeting certain areas. This could ultimately result in improved treatment outcomes for patients. Additional research and development are necessary to improve the synthesis methods and assess the effectiveness of these chemicals in clinical environments.
Distinct Frequently Asked Questions:
1). What is the significance of protein stabilizers in treating Gaucher disease?
Protein stabilizers aid in the correct folding and functioning of mutated glucocerebrosidase enzymes, targeting one of the fundamental causes of the disease.
2). What is the mechanism by which nitrone-derived isofagomines act as protein stabilizers?
Nitrone-derived isofagomines selectively bind to certain areas of mutant enzymes, facilitating their correct folding and stability. This, in turn, increases their therapeutic efficacy in treating Gaucher disease.
3). What difficulties arise while attempting to create nitrone-derived C5a-functionalized isofagomines?
Effective synthesis necessitates precise regulation of reaction parameters and careful choice of reagents to achieve optimal yields and purity of the end product. This presents difficulties in terms of scalability and efficiency.
4). What is the comparative efficacy of nitrone-derived isofagomines in treating Gaucher disease about current therapy options?
Nitrone-derived isofagomines provide a focused method for enhancing the stability of enzymes, which could potentially minimize unintended effects and enhance the effectiveness of treatments in comparison to conventional therapies.
5). What are the subsequent stages in the advancement of nitrone-derived isofagomines as therapeutic options for Gaucher disease?
Additional investigation is required to enhance the methods of combining substances, determine the effectiveness of compounds in studies conducted before clinical trials, and evaluate the safety and effectiveness of these compounds in patients over an extended period.
For more chemistry blogs, visit chemistry Master